AdaBoost Implementation
implementing AdaBoost from scratch and comparing it with Scikit-Learn's implementation along with exploring concept of early stopping and weighted errors in boosting algorithms.
The code demonstrates how to implement AdaBoost from scratch and compare it with Scikit-Learn’s implementation. It also explores early stopping and weighted errors in boosting algorithms.
Data Documentation
This data set dates from 1988 and consists of four databases: Cleveland, Hungary, Switzerland, and Long Beach V. It contains 76 attributes, including the predicted attribute, but all published experiments refer to using a subset of 14 of them. The “target” field refers to the presence of heart disease in the patient. It is integer valued 0 = no disease and 1 = disease.
For more information please read the data documentation.
Code Explanation
Data Preparation:
- Load the dataset from
heart_disease.csv. - Separate the target feature.
- Change class labels to 1 and -1.
- Perform train-test split.
Adaboost Algorithm Implementation:
- Define functions for calculating error and alpha.
- Initialize an
AdaBoostclass with empty lists for alphas, weak classifiers, and training errors. - Fit the model using a specified number of iterations (M).
- For each iteration:
- Set weights for the first iteration.
- Fit a weak classifier (simple tree with max depth 1).
- Calculate error and alpha for this classifier.
- Append the classifier, error, and alpha to their respective lists.
Prediction and Evaluation:
- Predict on test data using the trained model.
- Print evaluation metrics: accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
Scikit-Learn Implementation:
- Compare with Scikit-Learn’s AdaBoost implementation.
- Print evaluation metrics for Scikit-Learn model.
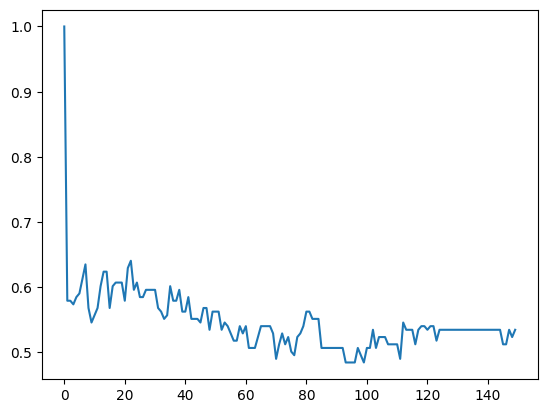
Early Stopping:
- Calculate validation error for different numbers of estimators.
- Plot validation error versus number of estimators.
- Determine the best number of estimators based on minimum mean squared error.
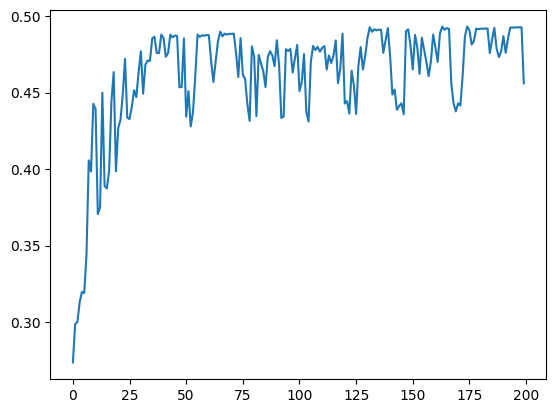
Weighted Error:
- Plot weighted training error versus number of estimators using training_errors attribute in AdaBoost class.
Adaboost
Introduction:
- AdaBoost (short for Adaptive Boosting) is an ensemble learning technique used for classification and regression.
- It combines multiple weak learners (usually decision trees) to create a strong classifier.
- The idea is to focus on samples that are misclassified by previous models.
Algorithm Steps:
- Initialization:
- Assign equal weights to all training samples.
- Initialize an empty set of weak classifiers.
- Iteration:
- For each iteration:
- Train a weak classifier on the weighted training data.
- Compute the error (weighted misclassification rate) of the classifier.
- Calculate the weight of the classifier based on its error.
- Update sample weights: increase weights of misclassified samples and decrease weights of correctly classified samples.
- Add the classifier to the ensemble with its weight.
- For each iteration:
- Final Model:
- Combine all weak classifiers into a strong ensemble model.
Prediction:
- To make predictions for a new sample:
- Weighted majority vote of weak classifiers.
- Higher weight classifiers have more influence.
Advantages:
- Simple and effective.
- Handles both binary and multiclass problems.
- Reduces bias and variance.