Handwritten Digit Classification
Handwritten Digit Classification on MNIST dataset using Conventional Neural Network in PyTorch
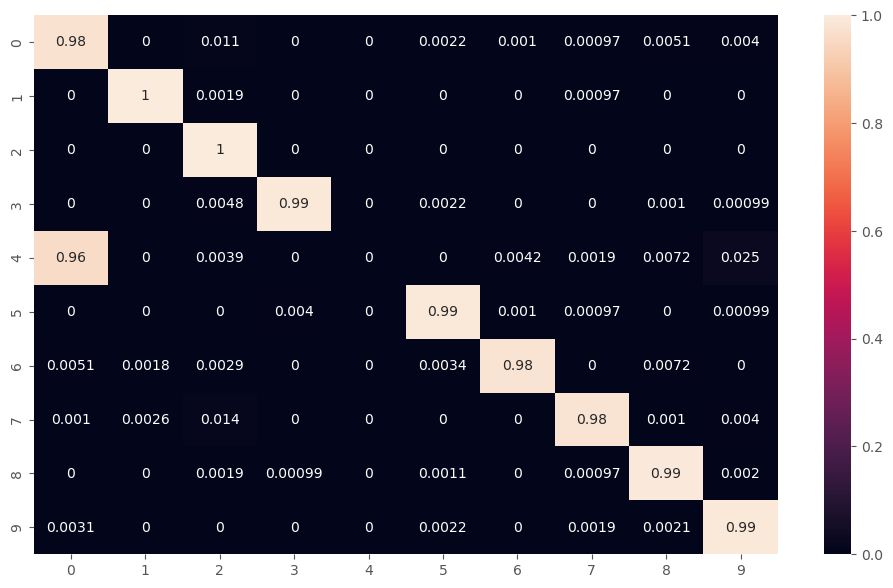
A code that uses PyTorch to build and implement a residual CNN for solving a classification problem. The goal is to classify handwritten digits from 0 to 9 on the MNIST dataset.
Data Documentation
The MNIST database of handwritten digits has a training set of 60,000 examples, and a test set of 10,000 examples.
Four files are available:
- train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz: training set images (9912422 bytes)
- train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz: training set labels (28881 bytes)
- t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz: test set images (1648877 bytes)
- t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz: test set labels (4542 bytes)
For more information please read the data documentation.
Code Explanation
-
Setup: A code block that imports the necessary libraries and modules, such as torch, torchvision, numpy, pandas, etc. It also sets the device to cuda if available, and defines the style for plotting.
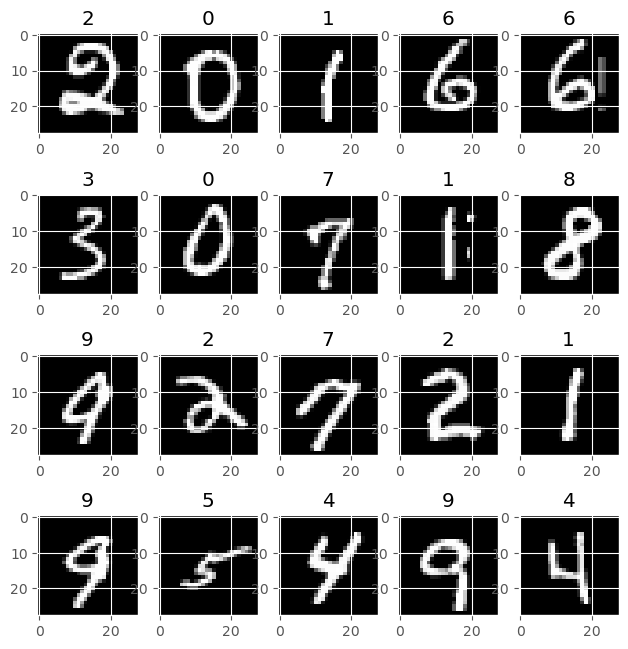
- Prepare The Data: A code block that defines a transformation to convert the images to tensors and normalize them. It also reads the MNIST dataset, splits it into train and validation sets, and creates dataloaders for them. It also plots some images from the train set.
- Define Model: A code block that defines a custom model class called ResidualClassifier. It inherits from nn.Module and implements a forward method. The model has several convolutional layers, max pooling layers, residual connections, an adaptive average pooling layer, a linear layer, and ReLU activations. It follows the architecture shown in the schematic diagram.
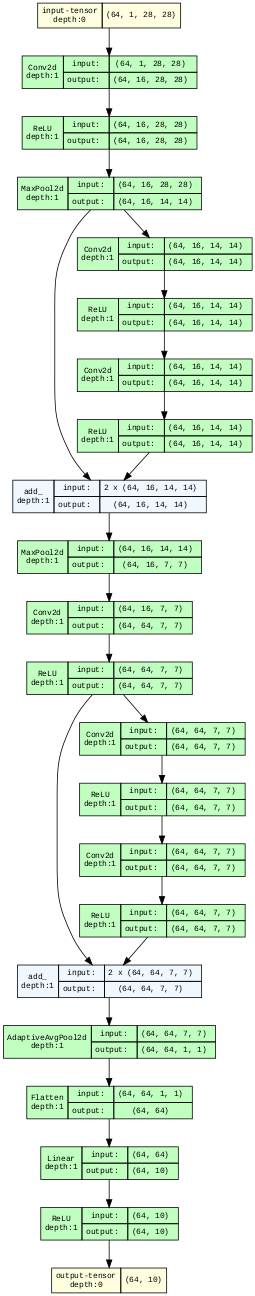
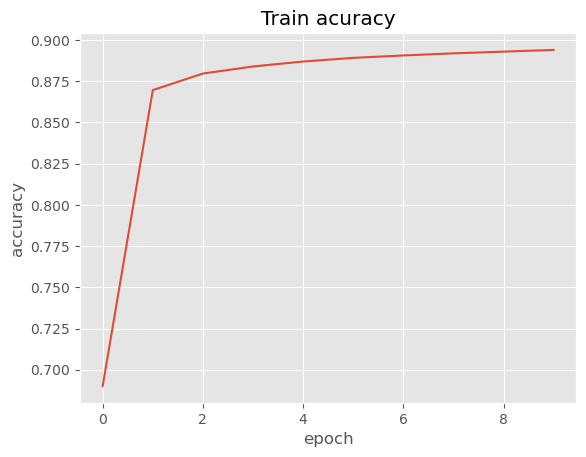
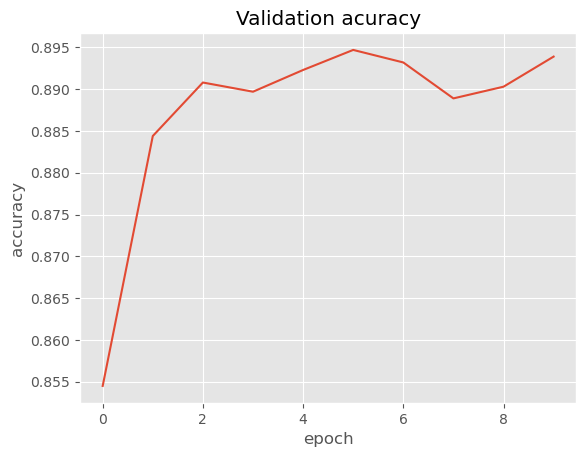
- Train Model: A code block that instantiates the model, defines the hyperparameters, optimizer, loss function, and other variables. It also defines a function to calculate the accuracy of the model. It then trains the model for several epochs, evaluates it on the validation set, and plots the loss and accuracy curves.